Nose, nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses Basicmedical Key
The medial wall separates the maxillary sinus from the nasal cavity, but they communicate throughout the ostium, located in the medial wall inferior or at the same level of the orbit floor. The inferior wall, known as the sinus floor, is in close relation with the posterior teeth apices, from which it is separated only by a layer of compact bone.

PPT Anatomy of Nose and Paranasal Sinus PowerPoint Presentation ID2646477
Each is a triangular space situated anterior to the limen nasi and defined laterally by the alae nasi, medially by the membranous septum—the distal end of the cartilaginous septum—and columella nasi, and inferiorly by the adjacent floor of the nasal cavity.

Nasal Cavity Nasal Cavity And Paranasal Sinus Cancer Miami Cancer Institute Baptist Health
The nasal cavity is lined with a mucous membrane (a lining of tissue) that makes mucus to help keep your nose moist and prevent nose bleeds from a dry nose. There are also little hairs, called cilia, on the inside walls of the nose that filter the air you breathe in to prevent dust and dirt from getting into your lungs.
Nariz y Cavidad Nasal Anatomía Concise Medical Knowledge
The medial wall, nasal wall, or base of maxillary sinus presents, in the disarticulated bone, a large, irregular aperture, communicating with the nasal cavity. In the articulated skull this aperture is much reduced in size by the following bones: the uncinate process of the ethmoid above, the ethmoidal process of the inferior nasal concha below, the vertical part of the palatine behind, and a.
The Nasal Cavity Structure Vasculature Innervation TeachMeAnatomy
The role of the nasal cavity is to humidify and warm the inspired air. Also, as the air passes through, the nasal cavity removes minute airborne particles and other debris before the air reaches the lower airways. Columnar epithelium lines the nasal cavity.
Nasal Cavity Anatomy
The lateral wall of each nasal cavity mainly consists of the maxilla. However, there is a deficiency that is compensated for by the perpendicular plate of the palatine bone, the medial pterygoid plate, the labyrinth of ethmoid and the inferior concha. The paranasal sinuses are connected to the nasal cavity through small orifices called ostia.
Easy Notes On 【Nasal Cavity】Learn in Just 4 Minutes! Earth's Lab
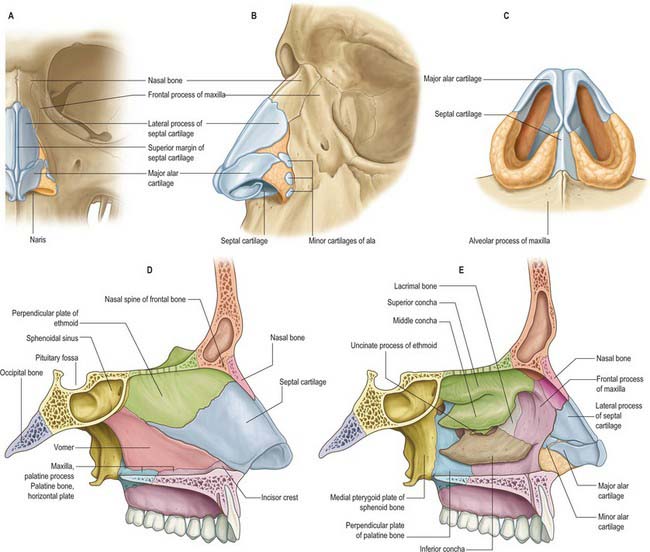
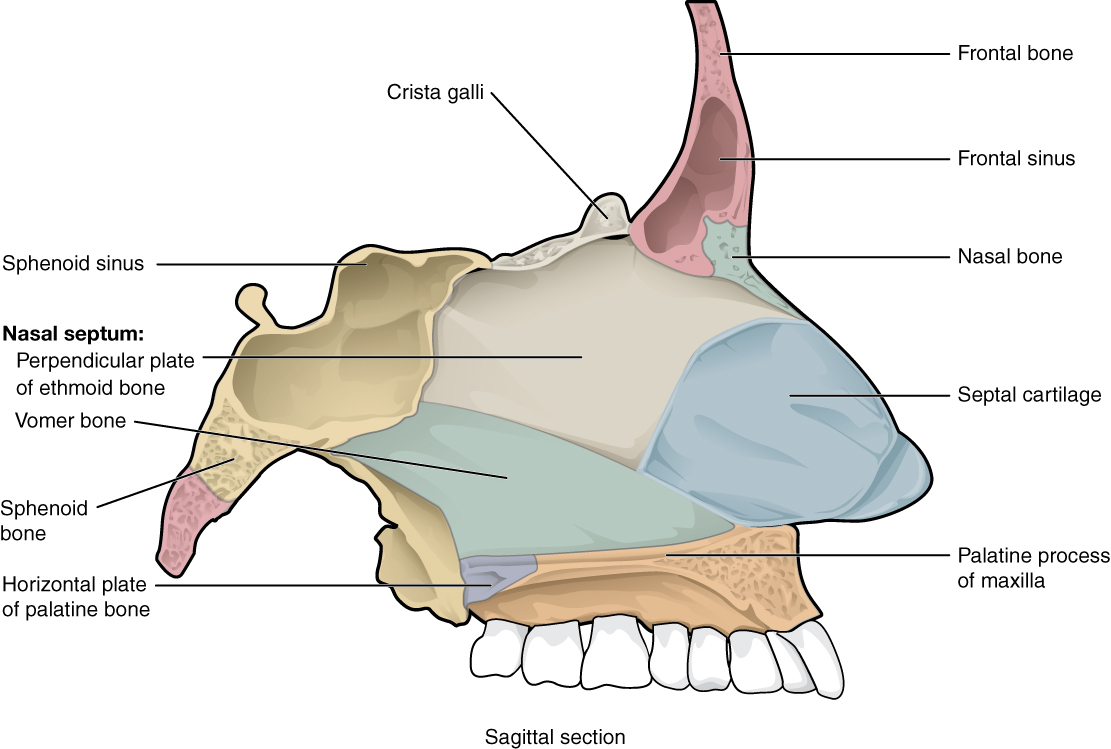
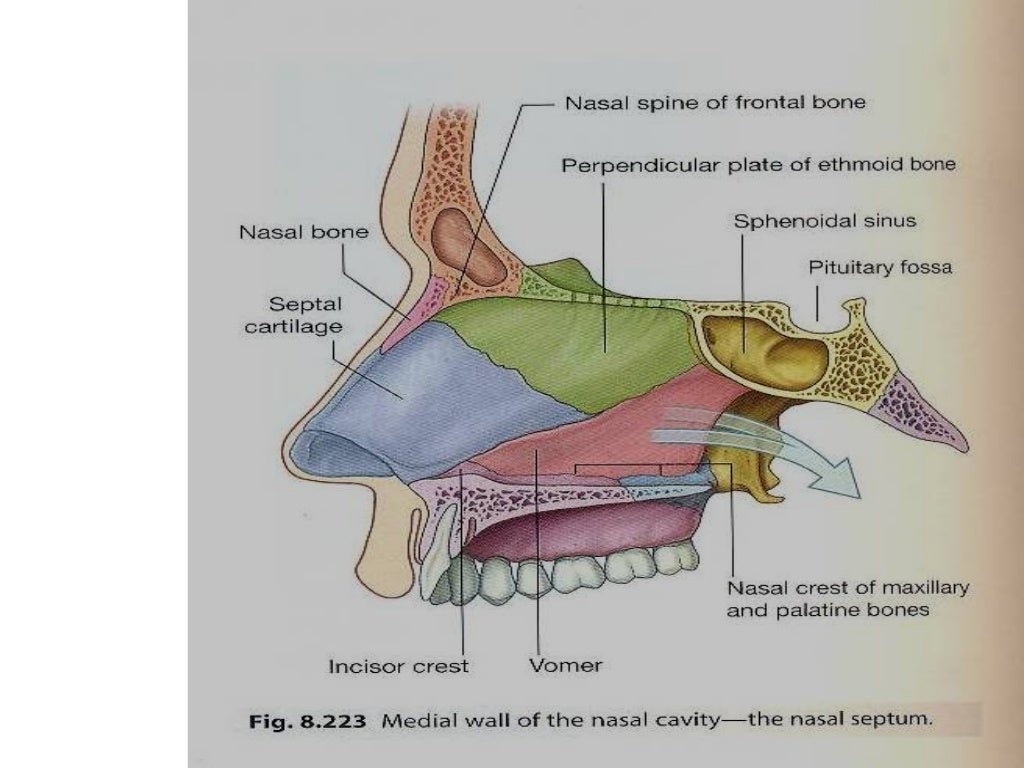
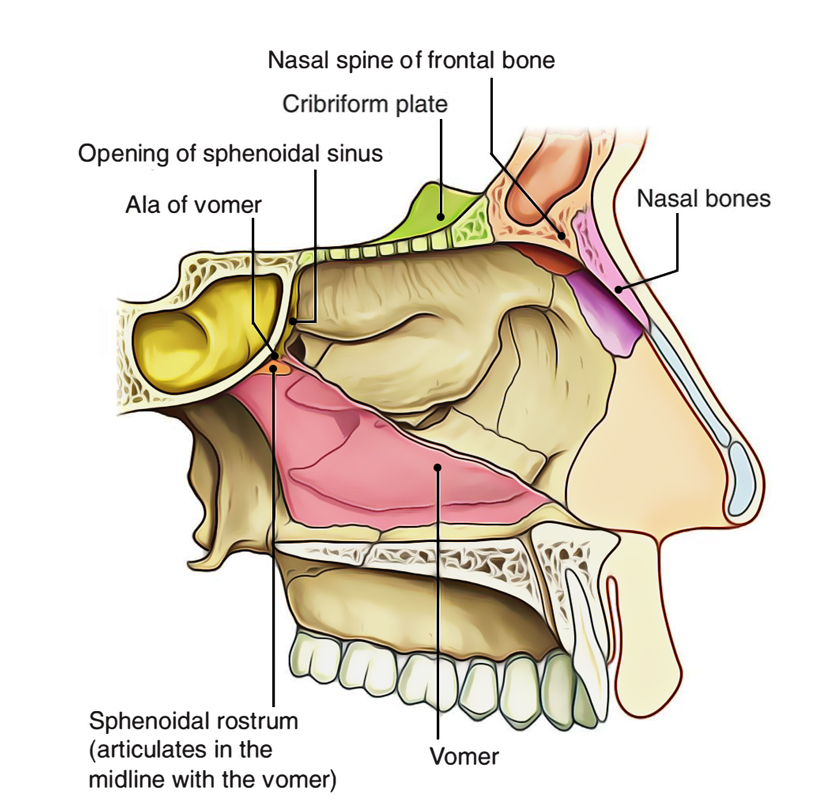
1.2 Medial Wall of Nasal Cavity: Nasal Septum The nasal septum is constituted by the septal cartilage and four bones: the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid, the vomer, septal crests of the palatine, and maxillary bones.

Nasal Cavity & Nose Atlas of Anatomy
The medial wall of the nasal cavity comprises the nasal septum, the septal cartilage and various bones of the skull. This article covers each structure and concludes with a summary of the the most important facts. Contents Nasal skeleton Ethmoid bone Maxillary bone Vomer Palatine bone Nasal cartilage and associated structures
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/6637/3eXjWpQKnS3a8LhBNJgWyQ_Lamina_cribrosa_01.png)
Medial wall of the nasal cavity Anatomy and structure Kenhub
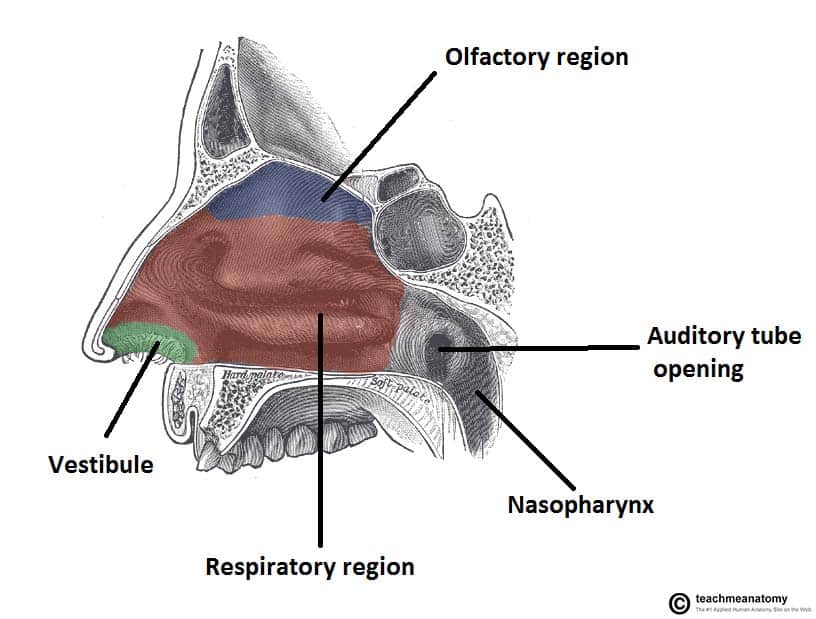
These pathways are called meatuses: Inferior meatus - between the inferior concha and floor of the nasal cavity. Middle meatus - between the inferior and middle concha. Superior meatus - between the middle and superior concha. Spheno-ethmoidal recess - superiorly and posteriorly to the superior concha.

Medial Wall of Nasal Cavity /Nasal Septum Bones & Cartilages Blood supply Nerve Supply
The largest part of the medial wall is from the ethmoid bone. The frontal process of the lacrimal fossa and the bony nasolacrimal canal are continuous and extend into the inferior meatus of the nasal cavity. The medial wall of the ethmoid bone is actually very thin and is called the lamina papyracea.

Medial wall of nasal cavity (nasal septum) anatomy images illustrations anatomy images
The medial wall of the nasal cavity is formed by the nasal septum. Anteriorly, it is continuous with the septal cartilage of the external nose. Posteriorly, it Is formed by the bony perpendicular plate of ethmoid (superiorly) and the vomer (inferiorly). Complete Anatomy The world's most advanced 3D anatomy platform Try it for Free
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/6641/6Q899gwjunuw5pat6riqg_Spina_nasalis_posterior_02.png)
Medial wall of the nasal cavity Anatomy and structure Kenhub
Welcome to our introductory video on the medial wall of the nasal cavity! Want more? Click here for the full video: https://khub.me/kkpui Shop the Kenhub - Learn Human Anatomy store $24.99.

Lateral aspect of the medial wall (nasal septum) of the right nasal cavity. Nasal septum
An in-depth understanding of the soft-tissue and neurovascular relationships of the maxillary sinus to the deep fascial spaces and branches of the trigeminal nerve and external carotid artery respectively is required to evaluate and report imaging involving the maxillary sinus.

Lateral Nasal Wall Medical school studying, Anatomy bones, Anatomy
The cranium (skull) is the skeletal structure of the head that supports the face and protects the brain. It is subdivided into the facial bones and the brain case, or cranial vault ( Figure 7.3 ). The facial bones underlie the facial structures, form the nasal cavity, enclose the eyeballs, and support the teeth of the upper and lower jaws.

Medial Wall of the Nasal Cavity (preview) Human Anatomy Kenhub YouTube
The nasal cavity, also known as the nasal fossa, forms part of the upper respiratory tract. Terminology Somewhat confusingly, the nasal cavity may refer to either the space either side of the nasal septum or the two spaces combined.

Nasal Cavity
The nasal cavity (Latin: cavitas nasi) is an irregular-shaped paired air-filled space located above the roof of the oral cavity. It forms the internal part of the nose. The nasal cavity is also an initial part of the respiratory system, and it lodges the olfactory receptors providing the sense of smell. Most of the nasal cavity is lined with.